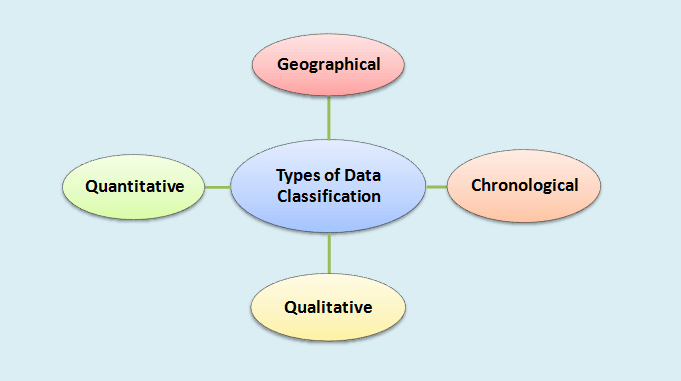
Types of Data Classification in Statistics:
Classification of data in statistics is the process of arranging the collected data into different homogeneous groups/classes and sub-classes, according to some common characteristics, properties, or criteria present in the data. Broadly, there are four types of classification of data; data can be classified on the following basis namely:
1. Geographical or Spatial Classification
2. Chronological or Temporal Classification
3. Qualitative Classification
4. Quantitative Classification
1. Geographical or Spatial Classification:
Geographical or Spatial Classification, i.e., area-wise classification, e.g., classification based on cities, districts, etc.
In geographical or spatial Classification, the data are classified by geographical regions or locations, like countries, states, territories, cities, villages, etc.
In other words, data are classified according to geographical or locational differences between the various items.
For example, when we present the production of sugar can, wheat, rice, etc., for various states, this would be called geographical classification.
2. Chronological or Temporal Classification:
Chronological or temporal Classification, i.e., classification based on time.
In chronological or temporal classification, the data are classified according to their time of occurrence, such as years, months, weeks, days, etc.
In other words, when you look at data over a long period of time, you can see how it changes over time, this type of classification is known as chronological classification.
For example, time-series; time-series are generally presented in chronological sequence, normally the earliest time period is used as the starting point.
3. Qualitative Classification:
Qualitative Classification, i.e., classification according to some attributes.
In qualitative classification, data are classified according to some attribute, quality or characteristics, such as gender, blood group, honesty, intelligence, literacy, colour, religion, marital status, etc.
In this type of classification, you can only find out whether or not it is present in the units of the studied population.
4. Quantitative Classification:
Quantitative Classification, i.e., classification according to magnitudes or classification in terms of numbers.
In quantitative classification, data are classified according to quantitative characteristics that can be measured, such as age, area, volume, height, width, length, weight, speed, humidity, temperature, prices, sales, income, year, the number of pets owned, marks, etc.
डेटा के वर्गीकरण के प्रकार (Types of Data Classification in Statistics in Hindi):
डेटा का वर्गीकरण डेटा में मौजूद कुछ सामान्य विशेषताओं, गुणों या मानदंडों के अनुसार एकत्रित डेटा को विभिन्न सजातीय समूहों/वर्गों और उप-वर्गों में व्यवस्थित करने की प्रक्रिया है।
मोटे तौर पर, डेटा को निम्नलिखित आधार पर वर्गीकृत किया जा सकता है:
1. भौगोलिक या स्थानिक वर्गीकरण
2. कालानुक्रमिक या सामयिक वर्गीकरण
3. गुणात्मक वर्गीकरण
4. मात्रात्मक वर्गीकरण
1. भौगोलिक या स्थानिक वर्गीकरण (Geographical or Spatial Classification):
भौगोलिक या स्थानिक वर्गीकरण, यानी क्षेत्रवार वर्गीकरण, जैसे, शहरों, जिलों आदि के आधार पर वर्गीकरण।
भौगोलिक या स्थानिक वर्गीकरण में, डेटा को भौगोलिक क्षेत्रों या स्थानों, जैसे देशों, राज्यों, क्षेत्रों, शहरों, गांवों आदि द्वारा वर्गीकृत किया जाता है।
दूसरे शब्दों में, डेटा को विभिन्न मदों के बीच भौगोलिक या स्थानीय अंतर के अनुसार वर्गीकृत किया जाता है।
उदाहरण के लिए, जब हम विभिन्न राज्यों के लिए चीनी केन, गेहूं, चावल आदि के उत्पादन को प्रस्तुत करते हैं, तो इसे भौगोलिक वर्गीकरण कहा जाएगा।
2. कालानुक्रमिक या सामयिक वर्गीकरण (Chronological or Temporal Classification):
कालानुक्रमिक या सामयिक वर्गीकरण, अर्थात समय के आधार पर वर्गीकरण।
कालानुक्रमिक या सामयिक वर्गीकरण में, डेटा को उनके घटित होने के समय के अनुसार वर्गीकृत किया जाता है, जैसे कि वर्ष, महीने, सप्ताह, दिन आदि।
दूसरे शब्दों में, जब आप लंबे समय तक डेटा का निरीक्षण करते हैं, तो आप देख सकते हैं कि यह समय के साथ कैसे बदलता है, इस प्रकार के वर्गीकरण को कालानुक्रमिक वर्गीकरण के रूप में जाना जाता है।
उदाहरण के लिए, समय-श्रृंखला (time-series): समय-श्रृंखला आमतौर पर कालानुक्रमिक क्रम में प्रस्तुत की जाती है, आमतौर पर प्रारंभिक बिंदु सबसे शुरुआती समय अवधिहोता है।
3. गुणात्मक वर्गीकरण (Qualitative Classification):
गुणात्मक वर्गीकरण, अर्थात् कुछ विशेषताओं के अनुसार वर्गीकरण।
गुणात्मक वर्गीकरण में, डेटा को कुछ विशेषता या गुणवत्ता या विशेषताओं के अनुसार वर्गीकृत किया जाता है, जैसे लिंग, रक्त समूह, ईमानदारी, बुद्धि, साक्षरता, रंग, धर्म, वैवाहिक स्थिति, आदि।
इस प्रकार के वर्गीकरण में, आप केवल यह पता लगा सकते हैं कि यह अध्ययन की गई जनसंख्या की इकाइयों में मौजूद है या नहीं।
4. मात्रात्मक वर्गीकरण (Quantitative Classification):
मात्रात्मक वर्गीकरण, यानी परिमाण के अनुसार वर्गीकरण या संख्याओं के संदर्भ में वर्गीकरण।
मात्रात्मक वर्गीकरण में, डेटा को मापे जा सकने वाले मात्रात्मक विशेषताओं के अनुसार वर्गीकृत किया जाता है, जैसे कि, उम्र, क्षेत्रफल, आयतन, ऊंचाई, चौड़ाई, लंबाई, वजन, गति, आर्द्रता, तापमान, मूल्य, बिक्री, आय, वर्ष, पालतू जानवरों की संख्या स्वामित्व, निशान, आदि।
(Source – Various books of college library)
Copyrighted Material © 2019 - 2024 Prinsli.com - All rights reserved
All content on this website is copyrighted. It is prohibited to copy, publish or distribute the content and images of this website through any website, book, newspaper, software, videos, YouTube Channel or any other medium without written permission. You are not authorized to alter, obscure or remove any proprietary information, copyright or logo from this Website in any way. If any of these rules are violated, it will be strongly protested and legal action will be taken.






Be the first to comment