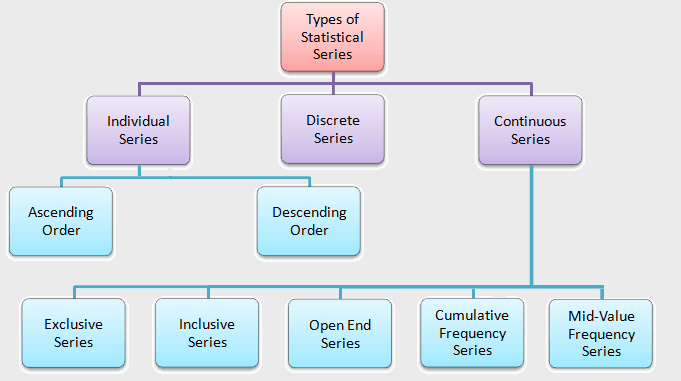
Open-End Class Interval:
In an Open-End interval, the lower limit of the first interval and/or the upper limit of the last interval is not given. Here, the length of these intervals is merely guessed based on the length of the interval nearest to them.
Assume the class intervals are as follows: “less than 20, 20-40, 40-60, 60-80, and more than 80″. These classes are open-end class intervals.
Open-End Classes:
The classification is called open-end classification if the lower limit of the first class, the upper limit of the last class, or both are not given, and such classes in which one of their boundaries (limits) is absent are called open-end classes. A frequency distribution with such classes is known as open-ended frequency distribution.
For example, the classes like the marks less than 20, marks more than 80, or age below 65 years, etc.
Open-End Series:
Open-end series is a kind of continuous series in which either the lower limit of the first class interval or the upper limit of the last class interval or both are absent.
For example, continuous series such as, “Less than 10, 10-20, 20-30, 30-40, 40-50, more than 50“; is called an Open-end series.
Purpose of using open-ended class intervals or classes:
- When the classes are not of equal width, an open-ended distribution is used. Because an open-ended distribution has an indeterminate first class interval at the beginning and/or an indeterminate last class interval at the end.
- When there are a limited number of items scattered over a long interval, grouped frequency distributions are kept open-ended.
Problem with using open-ended class intervals:
The use of open-end classes is not recommended generally. If possible, we avoid using open-end classes.
- The reason for avoiding using open-end classes is that the unavailability of limits makes it difficult to calculate problems. Without making an assumption, determining the mid-values of the first and last class intervals is hard. If the other closed class intervals have the same width, we can suppose that the open-end class intervals also have the same common width as the closed class intervals.
- Rigidly speaking, a histogram cannot be drawn for an open-ended distribution.
- For open-ended frequency distributions, the arithmetic mean is unsuitable.
- In the situation of an ‘open ends’ distribution, where the lower limit of the first class and the upper limit of the last class are not given, the range cannot be calculated.
- For distributions with open-ended classes, the mean deviation cannot be determined.
Open-end classes are classes with no lower or upper limit—for example, 65 years or more. However, because some data may contain just a few values that are either extremely high or extremely low in comparison to the others, such classes may not always be avoidable.
Open-end classes should be avoided as much as possible because the mid-value cannot be accurately determined in such classes. If open-ended classes are unavoidable, it is typical to estimate the class-mark or mid-value for the first class using the succeeding class as a guide. In other words, we assume that the size of the first and second classes are equal.
Example of an Open-End Series:
The following are the marks scored by the 20 students in a class out of a total of 100. If the marks scored by the 20 students in the class are given individually, it will form an Individual series, as shown follows:
90, 55, 35, 78, 51, 57, 60, 55, 55, 85, 78, 81, 35, 41, 61, 55, 62, 64, 55, 19.
This data can be represented in an open-end series as follows:
|
Marks (X) Class-intervals |
No. of Students
(Frequency f) |
|
Less than 20 |
1 |
|
20-40 |
2 |
|
40-60 |
8 |
| 60-80 |
6 |
| More than 80 |
3 |
| Total |
20 |
Open-End Class Interval in Hindi (खुले सिरों वाला वर्ग-अंतराल या मुक्त-अंत वर्ग-अंतराल):
खुले सिरों वाले अंतराल (Open-End interval) में, पहले अंतराल की निचली सीमा और/या अंतिम अंतराल की ऊपरी सीमा नहीं दी जाती है। यहां, इन अंतरालों की चौड़ाई का अनुमान केवल उनके निकटतम अंतराल की चौड़ाई के आधार पर लगाया जाता है।
मान लें कि वर्ग अंतराल इस प्रकार हैं: “20 से कम, 20-40, 40-60, 60-80, और 80 से अधिक“। ये वर्ग-अंतराल मुक्त-अंत वर्ग-अंतराल हैं।
Open-End Classes in Hindi (खुले सिरों वाले वर्ग (कक्षाएं) या मुक्त-अंत कक्षाएं):
यदि किसी वर्ग की नीचे या ऊपर की सीमा अनिश्चित है तो उसे खुले सिरों वाले वर्ग कहते है। दूसरे शब्दों में, यदि प्रथम कक्षा (वर्ग) की निचली सीमा, या अंतिम वर्ग की ऊपरी सीमा, या दोनों नहीं दिए गए हों, और ऐसे वर्ग जिनमें उनकी कम से कम एक सीमा अनुपस्थित हो, वे कक्षाएं खुले-सिरों वाले वर्गीकरण कहलाते हैं। इस तरह के वर्गों के साथ वितरण को खुले सिरों वाले आवृत्ति वितरण के रूप में जाना जाता है।
उदाहरण के लिए, कक्षाएं जैसे 20 से कम अंक, 80 से अधिक अंक, या 65 वर्ष से कम आयु आदि।
Open-End Series in Hindi (खुले सिरों वाली श्रेणी या मुक्त-अंत श्रेणी):
खुले सिरों वाली श्रृंखला (Open-end series) एक प्रकार की सतत श्रृंखला है जिसमें या तो प्रथम वर्ग अंतराल की निचली सीमा या अंतिम वर्ग अंतराल की ऊपरी सीमा या दोनों ही सीमाएं अनुपस्थित हैं।
उदाहरण के लिए, सतत श्रृंखला जैसे, “10 से कम, 10-20, 20-30, 30-40, 40-50, 50 से अधिक“; खुले सिरों वाली श्रृंखला कहलाती है।
खुले सिरों वाले वर्ग-अंतराल या कक्षाओं का उपयोग करने का उद्देश्य:
- जब कक्षाएं समान चौड़ाई की नहीं होती हैं, तो एक खुले-सिरों वाले वितरण (ओपन-एंडेड वितरण) का उपयोग किया जाता है। क्योंकि ओपन-एंडेड वितरण में शुरुआत में एक अनिश्चित प्रथम श्रेणी अंतराल होता है और/या अंत में एक अनिश्चित अंतिम वर्ग-अंतराल होता है।
- जब एक लंबे अंतराल में सीमित संख्या में आइटम बिखरे हुए होते हैं, तो समूहीकृत बारंबारता वितरण को ओपन एंडेड रखा जाता है।
खुले सिरों वाले वर्ग-अंतराल का उपयोग करने में समस्या:
आम तौर पर खुले सिरों वाले वर्ग-अंतराल के उपयोग की सलाह नहीं दी जाती है। यदि संभव हो तो हम खुले सिरों वाले वर्ग-अंतराल का उपयोग करने से बचते हैं। कोशिश यही होनी चाहिए कि खुले सिरों वाले वर्गों को ख़त्म कर दे या हटा दे।
- खुले सिरों वाले वर्ग-अंतराल का उपयोग करने से बचने का कारण यह है कि सीमाओं की अनुपलब्धता से समस्याओं की गणना करना मुश्किल हो जाता है। अनुमान लगाए बिना, प्रथम और अंतिम वर्ग अंतराल के मध्य-मानों को सही-सही निर्धारित करना कठिन है। यदि अन्य बंद वर्ग अंतरालों की चौड़ाई समान है, तो हम मान सकते हैं कि खुले सिरों वाले वर्ग अंतरालों में भी बंद वर्ग अंतराल के बराबर चौड़ाई होती है।
- दृढ़तापूर्वक बोलते हुए, एक खुले सिरों वाले वितरण के लिए एक हिस्टोग्राम तैयार नहीं किया जा सकता है।
- मुक्त-आवृत्ति वितरण के लिए, अंकगणितीय माध्य (arithmetic mean) अनुपयुक्त है।
- एक ‘खुले सिरे वाले’ वितरण की स्थिति में, जहां प्रथम श्रेणी की निचली सीमा और अंतिम वर्ग की ऊपरी सीमा नहीं दी जाती है, परिसर की गणना नहीं की जा सकती है।
- खुले सिरे वाले वर्गों वाले वितरण के लिए, माध्य विचलन निर्धारित नहीं किया जा सकता है।
खुले सिरे वाली कक्षाएं ऐसी कक्षाएं हैं जिनकी या तो कोई निचली सीमा नहीं है या कोई ऊपरी सीमा नहीं है – उदाहरण के लिए, 65 वर्ष या उससे अधिक। हालाँकि, क्योंकि कुछ डेटा में केवल कुछ मान शामिल हो सकते हैं जो दूसरों की तुलना में बहुत अधिक या बहुत कम होते हैं, इसलिए ऐसे वर्ग हमेशा टालने योग्य नहीं हो सकते हैं।
खुले सिरे वाली कक्षाओं से जितना हो सके बचना चाहिए क्योंकि इस तरह की कक्षाओं में मध्य-मानों का सही-सही निर्धारण नहीं किया जा सकता है। यदि खुले सिरे वाली कक्षाएं जरूरी हैं, तो प्रथम श्रेणी के लिए वर्ग-चिह्न या मध्य-मूल्य का अनुमान लगाने के लिए, अगली कक्षा का उपयोग एक मार्गदर्शक के रूप में करना चाहिए, यह मानते हुए कि पहली और दूसरी कक्षाओं का आकार बराबर है।
(Source – Various books from the college library)
Copyrighted Material © 2019 - 2024 Prinsli.com - All rights reserved
All content on this website is copyrighted. It is prohibited to copy, publish or distribute the content and images of this website through any website, book, newspaper, software, videos, YouTube Channel or any other medium without written permission. You are not authorized to alter, obscure or remove any proprietary information, copyright or logo from this Website in any way. If any of these rules are violated, it will be strongly protested and legal action will be taken.


Be the first to comment