Advantages and Disadvantages of Linear Programming Problem (LPP):
The advantages and disadvantages of Linear Programming Problem (LPP) are as follows:
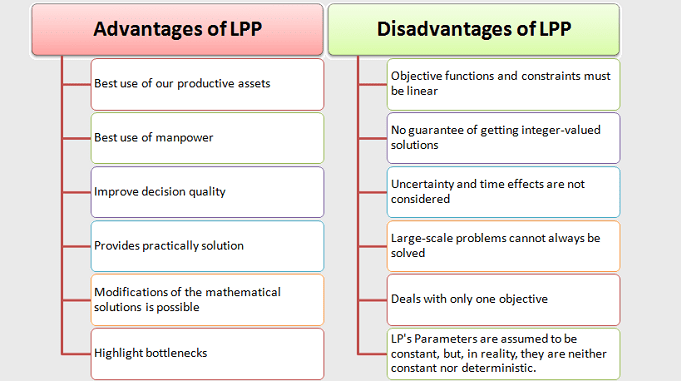
Advantages of Linear Programming Techniques:
- It enables us to make the best use of our productive assets.
That is, it advises how the available resources should be used optimally. It also explains how a decision-maker might successfully utilise his productive factors by choosing and allocating (distributing) these resources.
- It assists in making the best use of manpower and productive resources.
- Linear programming techniques improve decision quality also. The user’s decision-making approach becomes more objective and less subjective as a result of using this technique.
- It assists in the re-evaluation of a basic plan in the face of changing circumstances.
Read Also: Google’s AI chatbot “Google Bard” Vs “Chat GPT”: Which is better?
- LPP offers solutions that are realistic.
In other words, LP approaches provide acceptable and realistic solutions because there may be additional restrictions operating outside the problem that must be considered. For example, just because we have the capacity to make a large number of units does not imply that they can be sold. Thus, for the sake of ease to the decision-maker, the necessary modification of its mathematical solution is needed.
- Using linear programming, appropriate modifications to the mathematical solutions are also possible.
- It also reflects the limitations of the manufacturing process.
- The most notable advantage of this technique is the identification of barriers in manufacturing processes. When a barrier occurs, for example, some machines cannot meet demand while others sit idle for some of the time.
Disadvantages or Limitations of Linear Programming Techniques:
- The objective functions and constraints are not linear in some problems. In general, constraints are not treated linearly to variables, in real-life situations involving industrial and business challenges.
- There is no guarantee that you will get integer-valued solutions. For example, when determining how many people and machines are needed to do a specific task, rounding off the number to the nearest integer will not provide an optimal solution.
- The linear programming model does not take into account the effects of uncertainty and time.
- Even when a computer is available, large-scale problems cannot always be solved using linear programming techniques.
- The model’s parameters are considered to be constant. In reality, however, they are neither constant nor deterministic.
- Linear programming is concerned with only one objective.
Requirements for LPP:
An LPP can be optimized if the following conditions are satisfied:
- There must be a well-defined objective function that can be optimized and can be expressed as a linear function of decision variables.
- There must be constraints on the amount or extent of attainment of the objective and these constraints must be capable of being expressed as linear equations or linear inequalities in terms of decision variables.
- There must be an alternate course of action.
- The decision variables should be inter-related and non-negative.
(Source – Various books from the college library)
Copyrighted Material © 2019 - 2024 Prinsli.com - All rights reserved
All content on this website is copyrighted. It is prohibited to copy, publish or distribute the content and images of this website through any website, book, newspaper, software, videos, YouTube Channel or any other medium without written permission. You are not authorized to alter, obscure or remove any proprietary information, copyright or logo from this Website in any way. If any of these rules are violated, it will be strongly protested and legal action will be taken.



Be the first to comment