Cancer Diagnosing or Screening:
What is Cancer Diagnosing and Screening, how do the doctors come to know, that the patient has cancer, that is, how to detect cancer early stage?
For cancer patients, only early diagnosis may provide a complete cure. According to research, the most common cancer in the world is a relentless disease that affects one in every five people by the age of 70. The good thing is that 99 percent of all cases can be cured if diagnosed and treated early enough. Cancer that is detected at an early stage, when it is not too large and has not spread, has a better chance of being successfully treated.
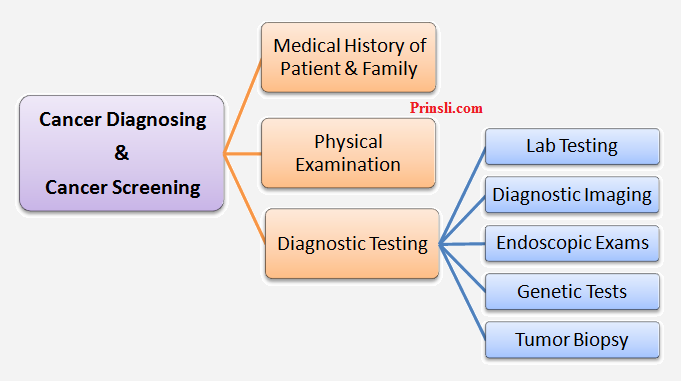
There is no single test for accurate diagnosing of cancer. Mostly, there are three ways to diagnose cancer, the complete medical history of the patient and their family, physical examination, and diagnostic testing.
In some conditions, it is necessary to retest and reevaluate the cancer patients, if the collected sample is not of good quality or gives unclear and inconclusive results or if the patient’s condition changed.
1. Medical History of Patient & Family:
There are various diseases, which are hereditary, so it is necessary to know about the family medical history of the patients. In addition, there are many symptoms which are common for cancer or other diseases.
2. Physical Examination:
In the next step of diagnosing, the oncologist does the patient physical examination. If the oncologist feels any lumps in the patient’s body, changes in skin colour, enlargement in any organs, or any other kinds of abnormalities, these symptoms indicate cancer.
3. Diagnostic Testing:
The final step to verify the cancer is diagnostic testing. Under the diagnostic procedure, there are mainly five following tests.
- Lab Tests,
- Diagnostic Imaging,
- Endoscopic Exams,
- Genetic Tests, &
- Tumor Biopsy.
(i) Lab Testing:
A laboratory test is a procedure, in which blood, urine, other body fluid or sometimes even tissue sample is collected from the patient for examination by the chemical process.
Some common laboratory tests in cancer cases are given below:
- Blood Chemistry Test,
- Cancer Gene Mutation Testing,
- Complete Blood Count (CBC),
- Cytogenetic Analysis,
- Immunophenotyping,
- Sputum Cytology,
- Tumor Marker Test,
(ii) Diagnostic Imaging:
In recent years, diagnostic radiology has progressed a lot with the new and advanced instruments and techniques, which help the oncologist detect accurate treatment regions for patient treatment. Imaging is the process of producing a picture of a patient’s body structure along with all the organs in detail. This imaging is used to find out the abnormalities, detect tumors (tumours), determine the extent of the disease, and for treatment evaluation. Imaging is used pre and post-surgery, pre & post-treatment also. There are various kinds of equipment for imaging the patients, as per requirement.
The names of some types of equipment are given below:
- X-Rays Imaging,
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan,
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI),
- Ultrasound,
- Positron Emission Tomography – Computed Tomography (PET-CT),
- Mammography.
(iii) Endoscopic Exam:
This is a procedure, in which a long flexible tube (endoscope) is inserted down the throat and into the esophagus. In this endoscope, a tiny camera is attached to collect the information on esophagus (oesophagus), stomach, and beginning of the small intestine for evaluation through an oncologist. There are various types of endoscopes, which are given below.
- Cystoscopy,
- Colonoscopy,
- Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP),
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy,
- Sigmoidoscopy
(iv) Genetic Test:
Genetic test helps to estimate the chances of developing cancer in the body. It is done by finding out the changes produced in genes, chromosomes, or proteins, called mutations.
A mutation is a change or alteration in an organism’s DNA sequence.
(v) Tumor Biopsy:
The biopsy is one of the most important and reliable tests for confirmation of cancer (malignant or any kind of infection). This is a procedure, which is performed to remove the tissue or cells from the body for examination under a microscope. The names of the most common biopsies are following-
- Endoscopic Biopsy,
- Bone Marrow Biopsy,
- Excisional or Incisional Biopsy,
- Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy,
- Punch Biopsy,
- Shave Biopsy,
- Skin Biopsy.
These are the general method, by which an oncologist confirms that the patient has cancer.
Fighting Cancer is Our Goal. Early detection saves lives.
Tags: what tests are done to check for cancer? early cancer detection test, can a doctor tell if you have cancer, how to detect cancer early, how do doctors tell patients they have cancer, what is biopsy test, can cancer be cured completely, benefits of early cancer detection, early cancer detection test, early diagnosis and treatment is which prevention. does early detection of cancer save lives, early cancer detection test? importance of early diagnosis, diagnosed with cancer, how is cancer diagnosed, how to diagnose cancer, how to detect cancer in early stage, cancer diagnosing, how can we diagnose cancer
Copyrighted Material © 2019 - 2024 Prinsli.com - All rights reserved
All content on this website is copyrighted. It is prohibited to copy, publish or distribute the content and images of this website through any website, book, newspaper, software, videos, YouTube Channel or any other medium without written permission. You are not authorized to alter, obscure or remove any proprietary information, copyright or logo from this Website in any way. If any of these rules are violated, it will be strongly protested and legal action will be taken.




Be the first to comment