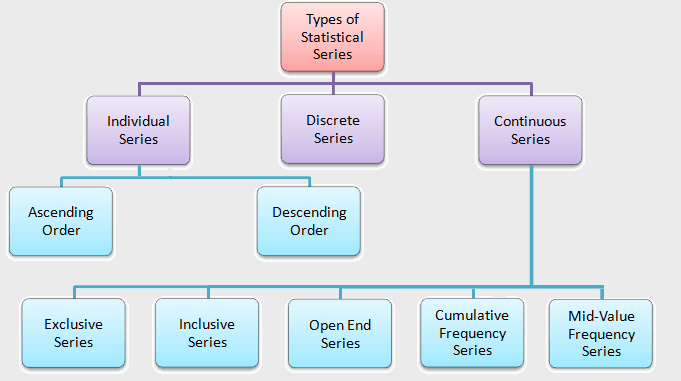
Cumulative Frequency Series in Statistics:
in statistics, Cumulative frequency series is a kind of continuous series in which the frequencies corresponding to each class interval in the series are added continuously. In this series, the frequency classes of different classes are not listed separately, but rather in a cumulative form, that is, the frequency in this form of series is cumulated rather than put against the interval corresponding to that one.
In a cumulative series to determine the frequency for a particular class, we either add or subtract the frequencies of all the previous class intervals. Furthermore, the classes are changed into ‘less than the upper limit‘ or ‘more than the lower limit.’
To solve a cumulative frequency series question, first, we convert the series from cumulative frequency to simple frequency.
When the cumulative frequency is given according to the upper limit, we write the words ‘less than‘ before each post value, and if it is given according to the lower limit, the words ‘more than‘ when the cumulative frequency is written.
Cumulative Frequency Distribution:
When the frequency of each class interval is cumulative, a frequency distribution becomes cumulative. The cumulative frequency of a class interval is computed by adding its frequency by the sum of the frequencies of the previous class intervals.
There are two different ways to convert any series into a cumulative frequency series. For example, let the class intervals be as follows:
5–10, 10–15, and 15–20.
(i) Then less than cumulative frequencies can be written using the class intervals’ upper limits, such as,
less than 10, less than 15, and less than 20.
(ii) And more than cumulative frequencies can be written using the class intervals’ lower class limits, such as,
more than 5, more than 10, and more than 15.
Types of Cumulative Frequency Series:
These series are of two types, e.g.,
- ‘Less than’ OR ‘Not above’,
- ‘More than’ OR ‘Not below’,
as given below:
Examples of cumulative frequency series:
The following series are Cumulative Series.
(1) ‘Less than’ / ‘Not above’ Cumulative frequency series
|
Class Interval |
f |
|
Less than 10 |
3 |
|
Less than 20 |
12 |
|
Less than 30 |
28 |
| Less than 40 |
49 |
| Less than 50 |
61 |
| Less than 60 |
68 |
| Less than 70 |
70 |
OR
|
Class Interval |
f |
|
Not above 10 |
3 |
|
Not above 20 |
12 |
|
Not above 30 |
28 |
| Not above 40 |
49 |
| Not above 50 |
61 |
| Not above 60 |
68 |
| Not above 70 |
70 |
(2) ‘More than’ or ‘Not Below’ Cumulative frequency series
| Class Interval | f |
|
More than 60 |
2 |
|
More than 50 |
9 |
|
More than 40 |
21 |
| More than 30 |
42 |
| More than 20 |
58 |
| More than 10 |
67 |
| More than 0 |
70 |
OR
| Class Interval | f |
|
Not below 60 |
2 |
|
Not below 50 |
9 |
|
Not below 40 |
21 |
| Not below 30 |
42 |
| Not below 20 |
58 |
| Not below 10 |
67 |
| Not below 0 |
70 |
(Source – Various books from the college library)
Copyrighted Material © 2019 - 2024 Prinsli.com - All rights reserved
All content on this website is copyrighted. It is prohibited to copy, publish or distribute the content and images of this website through any website, book, newspaper, software, videos, YouTube Channel or any other medium without written permission. You are not authorized to alter, obscure or remove any proprietary information, copyright or logo from this Website in any way. If any of these rules are violated, it will be strongly protested and legal action will be taken.


Be the first to comment