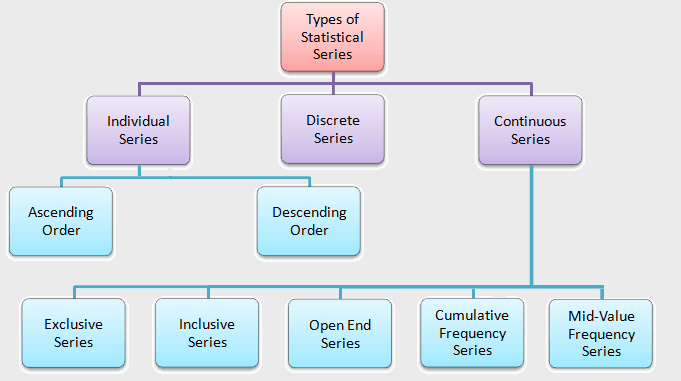
Individual Series in Statistics with Example:
In statistics, Individual Series are a kind of Statistical Series. The term “individual series” or “ungrouped data” refers to the same thing.
Individual series are those in which the frequencies are not given. An individual series is created when raw data is presented individually in the form of a series.
Individual Series, in other words, is a series of different individual observations, or a simple list of the items of each observation. Individual series is the individual arrangements of raw data. It provides numerical values for a particular case. Items in an individual series are displayed singly at a time. There is no class of items in such a series, and there is also no frequency of items.
These series cannot be classified or tabulated based on frequency. The value that occurs many times is written as many times as it appears separately. These are sorted either ascending or descending. In general, such series contain serial numbers, roll numbers, years, and names of locations or people. It is based upon the special fact that it contains only data values, not their frequencies.
Read Also: Discrete Series & Continuous Series in Statistics
Example of an Individual Series:
The following are the marks scored by the 20 students in a class out of a total of 100. If the marks scored by the 20 students in the class are given individually, it will form an Individual series, as shown follows:
90, 55, 34, 78, 51, 57, 60, 55, 55, 85, 70, 90, 35, 40, 60, 55, 60, 60, 55, 20.
Or,
The individual series can be arranged in two different ways:
(1) In Ascending Order:
Arranging data in increasing order, that is, arranging the data starting from the smallest value to the largest value, is known as ascending order. The data in the given example can be arranged as follows in ascending order:
20, 34, 35, 40, 51, 55, 55, 55, 55, 55, 57, 60, 60, 60, 60, 70, 78, 85, 90, 90.
Or,
(2) In Decreasing Order:
Arranging data in decreasing order, that is, arranging the data starting from the largest value to the smallest value, is known as descending order. The data in the given example can be arranged as follows in descending order:
90, 90, 85, 78, 70, 60, 60, 60, 60, 57, 55, 55, 55, 55, 55, 51, 40, 35, 34, 20.
Or,
Individual Series in Statistics with Example in Hindi
व्यक्तिगत श्रृंखला (Individual Series):
व्यक्तिगत श्रृंखला एक प्रकार की सांख्यिकीय श्रृंखला है। “व्यक्तिगत श्रृंखला” या “अवर्गीकृत डेटा”, दोनों शब्दों का मतलब एक ही है। एक प्रेक्षक जैसे ही कुछ आंकड़ों को या तथ्यों को देखता है उन्हें उसी रूप में लिख लेता है, इस प्रकार के आंकड़ों को ना तो वर्गों में बांटा जाता है और ना ही इन आंकड़ो में किसी प्रकार का कोई क्रम होता है।
व्यक्तिगत श्रृंखला वे श्रृंखला हैं जिनमें आवृत्तियाँ नहीं दी जाती हैं। जब अपरिष्कृत या कच्चे डेटा को एक श्रृंखला के रूप में व्यक्तिगत रूप से प्रस्तुत किया जाता है, तो इसे एक व्यक्तिगत श्रृंखला कहा जाता है।
दूसरे शब्दों में, व्यक्तिगत श्रृंखला, अलग-अलग व्यक्तिगत अवलोकनों की एक श्रृंखला है, अर्थात यह प्रत्येक अवलोकन की वस्तुओं की एक सरल सूची है। यह किसी विशेष स्थिति के लिए संख्यात्मक मान प्रदान करता है। एक व्यक्तिगत श्रृंखला में, आइटम एक बार में अकेले प्रदर्शित होते हैं। ऐसी श्रृंखला में वस्तुओं का कोई वर्ग नहीं होता है, और वस्तुओं की आवृत्ति भी नहीं होती है।
इन श्रृंखलाओं को आवृत्ति के आधार पर वर्गीकृत या सारणीबद्ध नहीं किया जा सकता है। बार-बार आने वाला मान अलग-अलग जितनी बार आता है उतनी ही बार लिखा जाता है। इन्हें या तो आरोही या अवरोही क्रम में व्यवस्थित किया जाता है। सामान्य तौर पर, ऐसी श्रृंखला में सीरियल नंबर, रोल नंबर, वर्ष और स्थानों या लोगों के नाम होते हैं। यह इस विशेष तथ्य पर आधारित है कि इसमें केवल डेटा मान होते हैं, उनकी आवृत्तियाँ नहीं।
व्यक्तिगत श्रृंखला का उदाहरण (Example of an Individual Series):
एक कक्षा में 20 छात्रों द्वारा, कुल 100 में से प्राप्त किए गए अंक (marks), निम्नलिखित हैं। यदि कक्षा में 20 छात्रों द्वारा प्राप्त अंक अलग-अलग दिए गए हैं, तो यह एक व्यक्तिगत श्रृंखला का निर्माण करेगा, जैसा कि नीचे दिखाया गया है:
90, 55, 34, 78, 51, 57, 60, 55, 55, 85, 70, 90, 35, 40, 60, 55, 60, 60, 55, 20.
या,
व्यक्तिगत श्रृंखला को दो अलग-अलग तरीकों से व्यवस्थित किया जा सकता है:
(1) आरोही क्रम में (In Ascending Order):
आँकड़ों को बढ़ते क्रम में व्यवस्थित करना, अर्थात् आँकड़ों को सबसे छोटे मान से सबसे बड़े मान तक व्यवस्थित करना आरोही क्रम कहलाता है। दिए गए उदाहरण में डेटा को आरोही क्रम में निम्नानुसार व्यवस्थित किया जा सकता है:
20, 34, 35, 40, 51, 55, 55, 55, 55, 55, 57, 60, 60, 60, 60, 70, 78, 85, 90, 90.
या,
(2) अवरोही क्रम में (In Decreasing Order):
आँकड़ों को घटते क्रम में व्यवस्थित करना, अर्थात् आँकड़ों को सबसे बड़े मान से सबसे छोटे मान तक व्यवस्थित करना अवरोही क्रम कहलाता है। दिए गए उदाहरण में डेटा को अवरोही क्रम में निम्नानुसार व्यवस्थित किया जा सकता है::
90, 90, 85, 78, 70, 60, 60, 60, 60, 57, 55, 55, 55, 55, 55, 51, 40, 35, 34, 20.
या,
(Source – Various books from the college library)
Tags: write example with solution of individual series in statistics
Copyrighted Material © 2019 - 2024 Prinsli.com - All rights reserved
All content on this website is copyrighted. It is prohibited to copy, publish or distribute the content and images of this website through any website, book, newspaper, software, videos, YouTube Channel or any other medium without written permission. You are not authorized to alter, obscure or remove any proprietary information, copyright or logo from this Website in any way. If any of these rules are violated, it will be strongly protested and legal action will be taken.





Be the first to comment