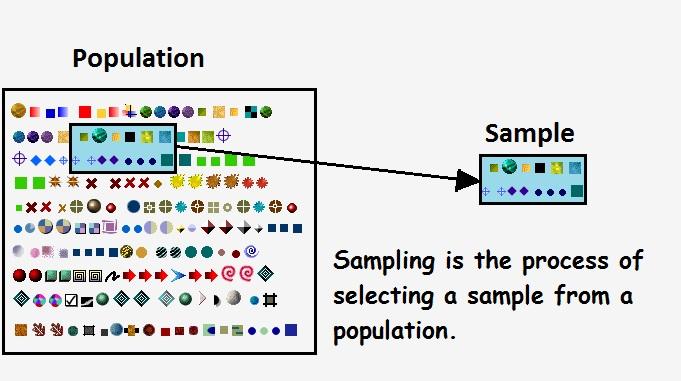
Definition of Population, Sample and Sampling in Statistics
Before discussing the concept of sampling in statistics, first, we will first define the population and sample.
♦ Population or Universe:
In statistics, the population is referred to as a whole, that is, it is an entire collection of objects, living or nonliving, that are being studied. It can be a group of people, items, events, organisations, etc. In other words, a population is the complete set of items which are of interest in any particular situation. For example, the group of all students of a university is a population. You use populations to draw conclusions. In a population, the number of elements may be finite or infinite.
Researchers and Statisticians like to study the characteristics of each entity in a population often to reach the most accurate conclusions possible.
It is obvious that for any statistical investigation complete enumeration of the population is rather impracticable most of the time since population sets tend to be quite large. The effort, money and time required for carrying out complete enumeration will generally be extremely large, and, in many cases, the cost may be so prohibitive that the very idea of collecting information by this method may have to be dropped.
For example, if we want to know the average per capita (monthly) income in a country, we must first identify all of the earning individuals in the country, which is rather a very difficult task. Similarly, complete enumeration is impossible if the population is infinite.
In this case, we take the help of sampling. Unless the information is required for each and every unit in the domain of study, the sampling technique is generally used to obtain the information.
♦ Sample:
A sample is a finite subset of statistical individuals in a population. A sample is a subset of individuals from a larger population. That is, a sample is only a part or subset of a population.
The sample size is defined as the number of individuals (elements) in a sample.
♦ Sampling:
The process of selecting a sample from a population is known as sampling. In the sampling method, instead of studying every unit of the population, only a part of the population (sample) is studied and drawing conclusions for the entire population on that basis.
Obtaining information about an entire population is often extremely expensive or nearly impossible. So we take a representative sample of the population, instead.
The characteristics of a sample must be the same as those of the population it represents.
Hence, for the purpose of obtaining characteristics of a population, we observe the individuals in the sample only instead of enumerating the entire population. Then these sample characteristics are used to approximate or estimate the population.
For example, after checking a sample of a particular item, we decide whether to purchase or reject it.
The error that occurs in such estimation is called Sampling Error, and it is inherent that cannot be prevented in all sampling schemes. But sampling results in considerable gains, especially in time and cost not only in respect of making observations of characteristics but also in the subsequent handling of the data.
Despite the fact that much of the development in sampling theory has occurred in recent years, the concept of sampling is quite old. Sampling is frequently used in our everyday lives.
♦ Examples of Sampling:
(1) In a store, we evaluate the quality of sugar, lentils, rice, wheat or any other commodity by taking a handful of it from the bag and then deciding whether or not to buy it.
(2) A housewife normally tests the food to find if they contain the proper quantity of salt or sugar.
(3) A housewife examines only two or three grains of boiling rice to know, whether the rice is cooked or not.
(4) A doctor examines a few drops of blood and draws conclusions about the blood constitution of the whole body.
(5) A businessman places orders for materials by examining only a small sample of the same.
(6) A teacher may put questions to one or two students and find out whether the class as a whole is following the lesson.
In fact, the technique of sampling is used in almost every field, whether consciously or unconsciously.
♦ Purpose of Sampling:
A sample is not studied for the sake of being studied. The primary goal of its study is to draw conclusions about the population. In other words, sampling is merely a tool for knowing about the characteristics of the population by examining only a small portion of it.
- The values obtained from the study of a sample, like the mean, variance etc., are called ‘statistic.’
- Such values for the population, on the other hand, are referred to as “parameters.”
(Source – Various books from the college library)
Tags: population, sample and sampling in statistics, what is sample in statistics, difference population and sample in statistics, population and sample in statistics, what is sample in statistics, define sample in statistics, example of sample in statistics, sample meaning in statistics, sampling in statistics example, what is sampling in statistics
Copyrighted Material © 2019 - 2024 Prinsli.com - All rights reserved
All content on this website is copyrighted. It is prohibited to copy, publish or distribute the content and images of this website through any website, book, newspaper, software, videos, YouTube Channel or any other medium without written permission. You are not authorized to alter, obscure or remove any proprietary information, copyright or logo from this Website in any way. If any of these rules are violated, it will be strongly protested and legal action will be taken.



this is very helpful content for us.. thank you so much..