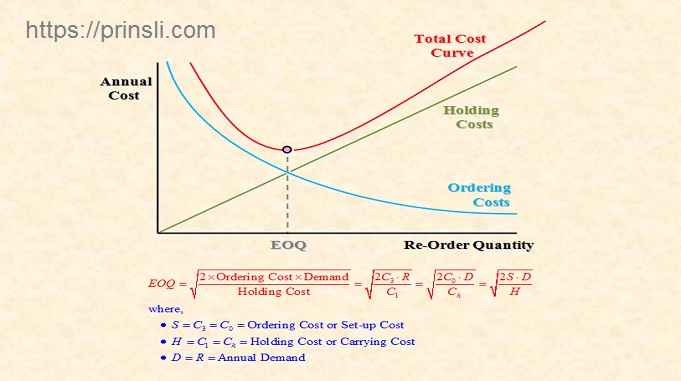
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ):
The concept of EOQ was first developed by F. Harris in 1916. In inventory management, economic order quantity (EOQ) is the order quantity that minimizes the total holding costs and ordering costs.
The concept is that management is confronted with a set of opposing costs-as the lot size (q) increases, the carrying charges (C1) will increase while the ordering costs (C3) will decrease. On the other hand, as the lot size (q) decreases, the carrying cost (C1) will decrease but the ordering costs will increase.
Thus, economic ordering quantity (EOQ) is that size of order which minimizes total annual (or other time period as determined by individual firms) cost of carrying inventory and cost of ordering under the assumed conditions of certainty and that annual demands are known.
Generally, economic order quantity is the point at which inventory carrying costs are equal to order costs. EOQ is that order quantity or optimal order size which minimizes the total cost.
The model is described under the following situations:
- Planning period is one year.
- Demand is deterministic and indicated by parameter D or R units per year.
- Cost of purchases, or of one unit is C.
- Cost of Ordering (or procurement cost of replenishment cost) is C3 or Co. For manufacturing goods, it is known as set-up cost.
- Cost of holding stock (also known as inventory carrying cost) is C1 or Ch per unit per year expressed either in items of cost per unit per period or in terms of percentage charge of the purchase price.
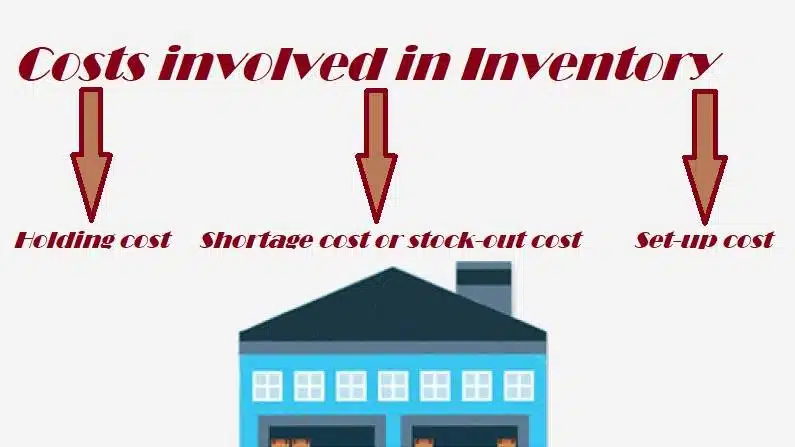
- Shortage cost (mostly it is back order cost) is C2 or Cs per unit per year.
- Lead time is L, expressed in unit of time.
- Cycle period in replenishment is t.
- Order size is Q.
In determining economic order quantity (eoq) it is assumed that cost of a managing inventory is made of solely of two parts i.e. ordering costs and carrying costs.
(A) Ordering Costs:
These are costs that are associated with the purchasing or ordering of materials. These costs include:
(1) Inspection costs of incoming materials.
(2) Cost of stationery, typing, postage, telephone charges etc.
(3) Expenses incurred on transportation of goods purchased.
These costs are also know as buying costs and will arise only when some purchases are made.
(B) Carrying Costs:
These are costs for holding the inventories. These costs will not be incurred if inventories are not carried. These costs include:
(1) The cost of capital invested in inventories. An interest will be paid on the amount of capital locked up in inventories.
(2) Cost of storage which could have been used for other purposes.
(3) Insurance Cost
(4) Cost of spoilage in handling of materials
EOQ is determined by the following formula:
Assumptions of EOQ:
While calculating EOQ the following assumptions are made.
- The supply of goods is satisfactory. The goods can be purchased whenever these are needed.
- The quality to be purchased by the concern is certain.
- The prices of goods are stable. It results to stabilize carrying costs.
Advantages of EOQ:
The advantages of EOQ are as follows:
- The advantage is that the EOQ model provides specific numbers particular to the business regarding inventory on hand, when to re-order, and how many to re-order. In turn, this limits the amount of re-stocking and results in better customer service.
- Another advantage is that the EOQ model is the customized recommendation regarding the most economical number of units to order.
Disadvantages of EOQ:
The disadvantages of EOQ are as follows:
- A key disadvantage to the EOQ model is it involves complicated math calculations.
- A further disadvantage is that EOQ models are based on assumptions.
- It also does not account for seasonal or economic fluctuations.
(Source – Various books of college library)
Copyrighted Material © 2019 - 2024 Prinsli.com - All rights reserved
All content on this website is copyrighted. It is prohibited to copy, publish or distribute the content and images of this website through any website, book, newspaper, software, videos, YouTube Channel or any other medium without written permission. You are not authorized to alter, obscure or remove any proprietary information, copyright or logo from this Website in any way. If any of these rules are violated, it will be strongly protested and legal action will be taken.



Be the first to comment