What is Gravity?
What is gravity, and its definition? – When you jump up, why do you just land on the ground instead of drifting off into space? Why do objects fall to the ground when you throw or drop them? The answer is Gravity, which is an invisible force that draws things toward each other. The gravity of the Earth is what keeps you on the ground and causes things to fall.
The force of attraction between any two objects in the universe is Gravity. Gravity is one of the fundamental forces of nature that pulls all matter in the universe. It is one of the four fundamental forces of nature, along with electromagnetism, the strong nuclear force, and the weak nuclear force.
Gravity is responsible for the motion of planets, stars, galaxies, and other celestial bodies. It is what keeps the Earth and other planets in orbit around the sun. Gravity is also responsible for tides and many other natural phenomena. The force of gravity is a fundamental force in nature and plays a crucial role in the dynamics of our solar system and the universe as a whole.
Gravity is a weak force compared to the other fundamental forces, but it has an infinite range. This means that it affects all objects in the universe, no matter how far apart they are.
Definition of Gravity
Gravity Definition – The force by which a planet or other celestial body pulls objects toward its center is called Gravity. The force of gravity keeps every planet in its orbit around the sun.
Force of Gravity – The force of gravity is the force by which a planet or other massive body attracts objects toward its center.
Gravity is responsible for keeping the planets in orbit around the sun, and for keeping the moon in orbit around the Earth. That is, gravity is the force that causes planets to orbit around their stars and the moon orbiting the Earth.
Strength of Gravity
Anything that has mass also has gravity. The strength of gravity depends on the mass of the objects and the distance between them. The force of gravity is proportional to the mass of the object and the distance between the object and the center of the planet.
In other words, Gravity is a fundamental force of nature that governs the behavior of objects in the universe. It is the force that causes two objects to attract each other based on their mass and distance.
Objects with more mass have more gravity. Gravity also gets weaker with distance. So, the greater the mass of an object, the stronger its gravitational pull. The closer objects are to each other, the stronger their gravitational pull is.
Read Also – What is an Exoplanet? Exploring the Definition, Types, and Discovery of Exoplanets
Gravity according to Newton
Gravity was first described by Sir Isaac Newton in his famous law of universal gravitation.
According to Newton’s law of universal gravitation, every particle in the universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
In other words, gravity is directly proportional to the mass of the objects and inversely proportional to the distance between them.
This means that the more massive an object is, the stronger its gravitational pull. Similarly, the closer two objects are to each other, the stronger their gravitational attraction.
That is, the greater the mass of the objects and the closer they are to each other, the stronger the force of gravity between them.
Theory of Gravity according to Albert Einstein
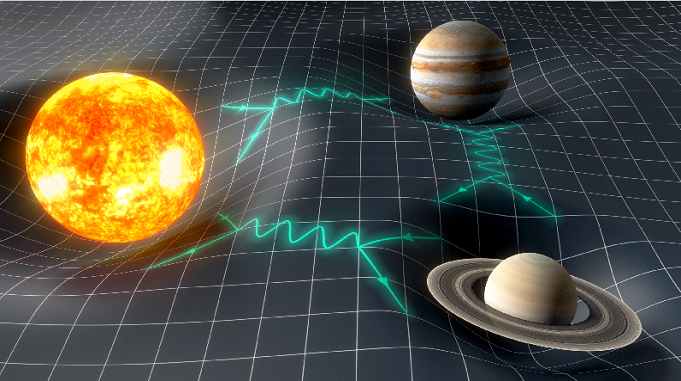
The theory of gravity was further refined by Albert Einstein‘s theory of general relativity. According to this theory, gravity is not a force that acts between objects but is instead the result of the curvature of space-time caused by the presence of mass and energy.
Einstein’s Theory of General Relativity – One of the key implications of general relativity is that gravity can also affect the behavior of light. When light passes near a massive object, its path is bent by the curvature of space-time. This effect is known as gravitational lensing and is a powerful tool used by astronomers to study distant galaxies and other celestial objects.
Gravity can also bend the fabric of space and time. This is called gravitational lensing and has been observed by astronomers using powerful telescopes.
In other words, mass and energy warp the fabric of space-time, and this curvature causes objects to move along curved paths.
In short, Albert Einstein described gravity as a curve in space that wraps around an object—such as a star or a planet. If another object is nearby, it is pulled into the curve.
The reason gravity pulls you toward the ground is that all objects with mass, like our Earth, actually bend and curve the fabric of the universe, called spacetime. That curvature is what you feel as gravity. (Source – NASA)
Interesting facts about Gravity
♦ Planets are spherical because of gravity. The gravity of a planet pulls evenly from all sides. Like the spokes of a bicycle wheel, gravity pulls from the center to the edges. This results in a planet’s overall shape being a sphere (or nearly spherical), which is a circle in three dimensions.
♦ Astronauts discovered that “A candle flame is spherical (round) and blue in zero gravity,” when they lit candles on NASA’s Skylab space station in the 1970s.
Conclusion
In summary, gravity is a fundamental force of nature that causes objects with mass to attract each other based on their mass and distance. That is, gravity is responsible for the attraction between objects in the universe. It is directly proportional to the mass of the objects and inversely proportional to the distance between them.
Gravity is what keeps the planets in orbit around the sun and has an infinite range. It is responsible for the behavior of planets, stars, and galaxies, and its effects are described by both, Newton’s law of universal gravitation and Einstein’s theory of general relativity.
Tags: what is the force of gravity with the definition? what is gravity with the definition?
Copyrighted Material © 2019 - 2024 Prinsli.com - All rights reserved
All content on this website is copyrighted. It is prohibited to copy, publish or distribute the content and images of this website through any website, book, newspaper, software, videos, YouTube Channel or any other medium without written permission. You are not authorized to alter, obscure or remove any proprietary information, copyright or logo from this Website in any way. If any of these rules are violated, it will be strongly protested and legal action will be taken.




Be the first to comment