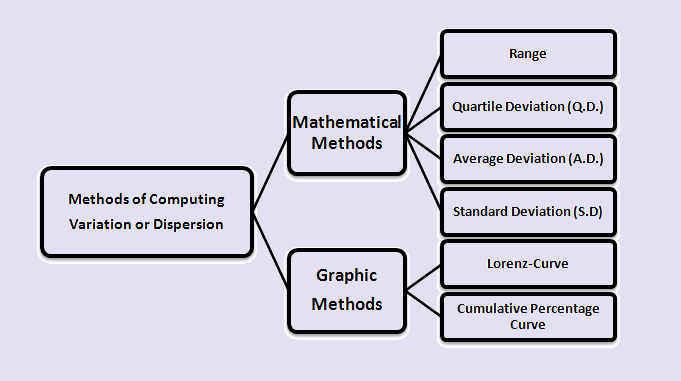
Methods of Computing Variation or Dispersion:
Although the mean and other measures are useful in identifying the central tendency of values in data, it is also valuable to describe their dispersion or scatter.
To reveal the degree of the spread out or the extent of the variability in individual items of the distribution can be known by certain other measures, known as ‘Measures of Dispersion’ or ‘Measures of Variation’. The Variation or dispersion of a distribution refers to the amount of scattering in the values.
Methods of Computing Variation or Dispersion are divided into two types:
(1) Mathematical Methods:
These methods are used to study the ‘degree’ and ‘extent’ of variance. The following are some of the most widely used measures of Variation or dispersion in this category:
(a) Range:
It’s the simplest way to figure out how dispersion works. The range of a series is the difference between its smallest and largest values.
(b) The Interquartile Range or Quartile Deviation (Q.D.):
Another name for Quartile Deviation is the Inter-quartile range. Only the values of the ‘Upper quartile’ (Q3) and the ‘Lower quartile’ (Q1) are considered in the concept of ‘Quartile Deviation’.
This is a much better way when we want to know the range within which a certain proportion of the items fall. The ‘Quartile Deviation’ is calculated as follows:
Inter-quartile range = Q3 – Q1.
(c) Mean deviation or Average Deviation (A.D.):
Mean deviation or Average Deviation is defined as a value calculated by averaging the deviations of various items from a measure of central tendency (Mean, Median, or Mode), after ignoring negative signs.
(d) Standard Deviation (S.D.) and Coefficient of Variation:
The positive square root of the variance is called the Standard Deviation. The square root of the average of squared deviations taken from the actual mean is used to find the standard deviation. It is denoted by the Greek letter σ (read as sigma).
When comparing two or more series, the coefficient of variation is commonly used.
(2) Graphic Methods:
Lorenz-Curve or Cumulative Percentage Curve is used where we want to study only the extent of variation, whether it is greater or lesser.
Methods of Computing Variation or Dispersion in Hindi
विचरण (प्रसार) या प्रकीर्णन (अपकिरण) की गणना के तरीके:
यद्यपि माध्य और अन्य माप डेटा में मूल्यों की केंद्रीय प्रवृत्ति की पहचान करने में उपयोगी होते हैं, लेकिन उनके फैलाव, प्रसार या बिखराव की विशेषताओं का वर्णन करना भी महत्वपूर्ण है।
वितरण की प्रत्येक व्यक्तिगत अलग-अलग मदों में विचलन की डिग्री, मात्रा या परिवर्तनशीलता की सीमा को, विभिन्न प्रकार की अन्य मापों, जैसे – विचरण की मापें (Measures of Variation) या प्रकीर्णन की मापें (Measures of Dispersion), के द्वारा ज्ञात किया जा सकता है। यहाँ विचरण (प्रसार) या प्रकीर्णन (अपकिरण) शब्द, किसी वितरण की आंकड़ों में बिखराव की मात्रा को संदर्भित करता है।
विचरण या प्रकीर्णन की गणना की विधियों को दो भागों में विभाजित किया गया है:
(1) गणितीय विधियां:
इन विधियों का उपयोग विचरण (Variation) या प्रकीर्णन (Dispersion) की ‘डिग्री’ और ‘सीमा’ का अध्ययन करने के लिए किया जाता है। इस श्रेणी में विचरण या प्रकीर्णन के कुछ सबसे व्यापक रूप से उपयोग किए जाने वाले उपाय निम्नलिखित हैं:
(a) विस्तार (Range):
यह विचरण या प्रकीर्णन का पता लगाने का सबसे आसान और शुरुआती तरीका है कि फैलाव कैसा है। एक श्रेणी का परिसर या विस्तार उसके सबसे छोटे और सबसे बड़े मूल्यों के बीच का अंतर है।
(b) अंतर-चतुर्थक विस्तार या चतुर्थक विचलन (Q.D.):
चतुर्थक विचलन का दूसरा नाम अंतर-चतुर्थक विस्तार है। ‘चतुर्थक विचलन’ की अवधारणा में केवल ‘उच्चतम चतुर्थक’ (Q3) और ‘निम्नतम चतुर्थक’ (Q1) के मूल्यों पर विचार किया जाता है।
यह एक बेहतर तरीका है जब हम उस सीमा को जानना चाहते हैं जिसके भीतर वस्तुओं का एक निश्चित अनुपात है। ‘चतुर्थक विचलन’ की गणना इस प्रकार की जाती है:
अंतर-चतुर्थक विस्तार = Q3 – Q1.
(c) माध्य विचलन या औसत विचलन (A.D.):
केंद्रीय प्रवृत्ति (माध्य, माध्यिका, या बहुलक) की माप से श्रेणी के विभिन्न मूल्यों के विचलनों के माध्य द्वारा परिकलित मान, माध्य विचलन या औसत विचलन कहलाता है। माध्य विचलन की गणना में सभी विचलनों को धनात्मक लिया जाता है।
(d) मानक विचलन (S.D.) और विचरण का गुणांक:
प्रसरण (variance) का धनात्मक वर्गमूल मानक विचलन है। मानक विचलन की गणना करने के लिए, वास्तविक माध्य से लिए गए वर्ग विचलन के औसत का वर्गमूल उपयोग किया जाता है। इसे ग्रीक अक्षर σ (सिग्मा के रूप में पढ़ा जाता है) द्वारा दर्शाया गया है।
विचरण का गुणांक का उपयोग आमतौर पर दो या दो से अधिक श्रृंखलाओं की तुलना करते समय किया जाता है।
(2) ग्राफिक या बिंदु रेखीय विधियां:
लोरेंज-वक्र या संचयी-प्रतिशत-वक्र का उपयोग तब किया जाता है जब हम केवल विचरण या प्रकीर्णन के विस्तार का अध्ययन करना चाहते हैं, चाहे वह अधिक हो या कम, परन्तु इससे विचरण या प्रकीर्णन की ‘डिग्री’ ज्ञात करना संभव नहीं है।
(Source – Various books from the college library)
Copyrighted Material © 2019 - 2024 Prinsli.com - All rights reserved
All content on this website is copyrighted. It is prohibited to copy, publish or distribute the content and images of this website through any website, book, newspaper, software, videos, YouTube Channel or any other medium without written permission. You are not authorized to alter, obscure or remove any proprietary information, copyright or logo from this Website in any way. If any of these rules are violated, it will be strongly protested and legal action will be taken.

Be the first to comment