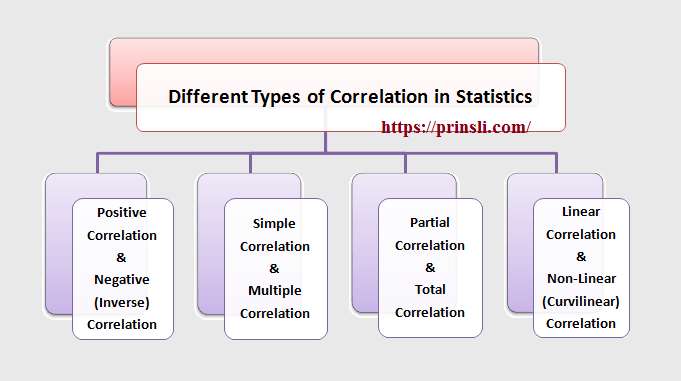
Different Types of Correlation in Statistics:
In statistics, four types of correlation are generally measured. Correlation in statistics can be classified into one of the following categories:
- Positive Correlation and Negative (Inverse) Correlation
- Simple Correlation and Multiple Correlation
- Partial Correlation and Total Correlation
- Linear Correlation and Non-Linear (Curvilinear) Correlation
(1) Positive and Negative Correlation:
- Positive or Direct Correlation: The movement of variables in the same direction is known as a positive or direct correlation. That is, when the values of both the variables either increase together or decrease simultaneously, the correlation is said to be positive.
- Negative or Inverse Correlation: The movement of the variables in the opposite direction is referred to as negative or inverse correlation. That is, if the value of one variable rises while the value of another falls, or if the value of one variable falls while the value of another rises, the correlation is said to be negative.
Read Also: Difference between correlation and causation
(2) Simple and Multiple Correlation:
- Simple Correlation: In simple correlation, we analyse the relationship between two variables only, i.e., between the production of wheat and the amount of rainfall, or between the demand and supply of a commodity.
- Multiple Correlation: The relationship between three or more variables is explored in the case of multiple correlation. For instance, the relationship of wheat production can be investigated with both chemical fertilisers and pesticides.
(3) Partial and Total Correlation:
Multiple correlation analysis can be divided into two categories: partial correlation and total correlation.
- Partial Correlation: In partial correlation, the relationship between two or more variables is studied, which considers only one dependent variable and one independent variable while keeping all others constant.
For instance, the coefficient of correlation between rice production and rainfall, excluding the effects of pesticides, chemical fertilisers and manures, is called partial correlation.
- Total Correlation: The total correlation is found by taking all of the variables.
(4) Linear and Non-Linear Correlation:
- Linear Correlation: The correlation is said to be linear when the amount of change in one variable tends to maintain a constant ratio to the amount of change in the other variable.
- Curvilinear or Non-linear Correlation: The correlation is said to be curvilinear or non-linear if the amount of change in one variable does not bear a constant ratio to the amount of change in the other variable.
The consistency of the ratio of change between the variables determines the distinction between linear and non-linear correlation.
(Source – Various books from the college library)
Copyrighted Material © 2019 - 2024 Prinsli.com - All rights reserved
All content on this website is copyrighted. It is prohibited to copy, publish or distribute the content and images of this website through any website, book, newspaper, software, videos, YouTube Channel or any other medium without written permission. You are not authorized to alter, obscure or remove any proprietary information, copyright or logo from this Website in any way. If any of these rules are violated, it will be strongly protested and legal action will be taken.

Be the first to comment