Variable in Statistics:
In algebra, a “variable” simply relates to an unknown value.
But in statistics, a variable is any characteristic recorded in a study. In other terms, the variables are any characteristics, numbers, or quantities that can be counted or measured, such as the number of hours per day that you play video games.
A variable, in the most obvious definition, is an entity whose value changes over time.
In statistics, there are almost dozens of different types of variables. Some types of variables are used more often than others. But in most cases, the word “variable” still means that we are dealing with something unknown, although that unknown is not always a number.
Variables are usually listed in a data set’s columns with rows indicating distinct observations on the variable. A variable is also known as a data item.
Examples of variables:
The term “variable” focuses on the fact that data values vary, that is, data values change throughout time. Business income and expenses, capital expenditure, business profits or losses, place of birth, class grades, hair colour, age, sex, vehicle type, etc. are all variables because their value varies between data units in a population and changes over time.
For example, to research whether global warming has occurred in your area, you may collect data on the highest daily temperature at the local meteorological station for the past century. In this case, the high temperature is the variable. The low temperature, whether it snowed that day, the number of centimetres of rainfall, cloud cover, etc. are some examples of the other variables for each day.
In statistics, a variable has two defining characteristics:
- A variable is a characteristic that identifies a person, location, item, or concept.
Hair colour, for example, is a variable that can be “blond” for one individual and “brunette” for another.
- The variable’s value can “vary” from one unit to the next.
For instance, ‘income’ is a variable that varies between data units in a population (i.e., the people or businesses being examined may not all have the same incomes) and also varies over time for each data unit (i.e. income can go up or down).
Importance of Variable:
A variable is an important part of every statistical data set. Because it is a speciality of a member of a particular sample or population that is unique, and distinct from other members of the same sample or population in terms of quantity or quality.
Variables are important because they help in the operationalization of concepts for data collection. We know that the method of strictly defining variables into measurable factors is called operationalization, where operationalization defines fuzzy ideas and enables them to be practically and statistically measured.
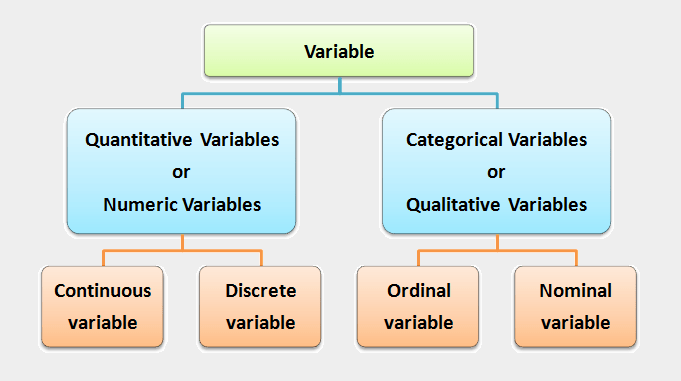
Types of Variables:
Variables might be categorical or quantitative. The data values that we observe for a variable are referred to as observations. Each observation can be a numerical value, such as the number of centimetres of rainfall in a day, or each observation can belong to a category, such as “yes” or “no” for whether it rained. There are two types of variables used in statistics:
(1) Quantitative Variables or Numeric Variables
Quantitative variables are also classified as either discrete or continuous variables, that is, there are two types of quantitative variables:
(i) Discrete variables,
(ii) Continuous variables.
(2) Categorical Variables or Qualitative Variables
Categorical variables are also classified as either nominal or ordinal variables, that is, there are two types of categorical variables:
(i) Nominal variables,
(ii) Ordinal variables.
(Source – Various books from the college library)
Read Also: Types of Data: Qualitative & Quantitative Data; Nominal, Ordinal, Discrete & Continuous Data
Copyrighted Material © 2019 - 2024 Prinsli.com - All rights reserved
All content on this website is copyrighted. It is prohibited to copy, publish or distribute the content and images of this website through any website, book, newspaper, software, videos, YouTube Channel or any other medium without written permission. You are not authorized to alter, obscure or remove any proprietary information, copyright or logo from this Website in any way. If any of these rules are violated, it will be strongly protested and legal action will be taken.

Be the first to comment